

On the next screen, you will be asked to allocate RAM to the VM. It is recommended to allocate at least 10GB of space for the VM. Give the VM a name and select an appropriate location for the virtual disk. In the “New Virtual Machine” window, select “Linux” as the operating system and “Other Linux (64-bit)” as the version. Once open, click on the “New” button to create a new virtual machine. The first step is to open the QEMU Manager application.
Finally, make sure to have the latest version of QEMU installed on your system. Secondly, create a separate hard drive partition for the VM to avoid any potential conflicts with the host operating system. Firstly, it is recommended to allocate at least 2GB of RAM to the VM. There are a few things to keep in mind before starting this process. Virtual machines can also be used to isolate sensitive data and systems from potential attacks. It allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine, which can be useful for software testing and development. Creating a virtual machine has a number of advantages. QEMU is a freely available and open-source processor emulator that enables users to create virtual machines on a variety of platforms.
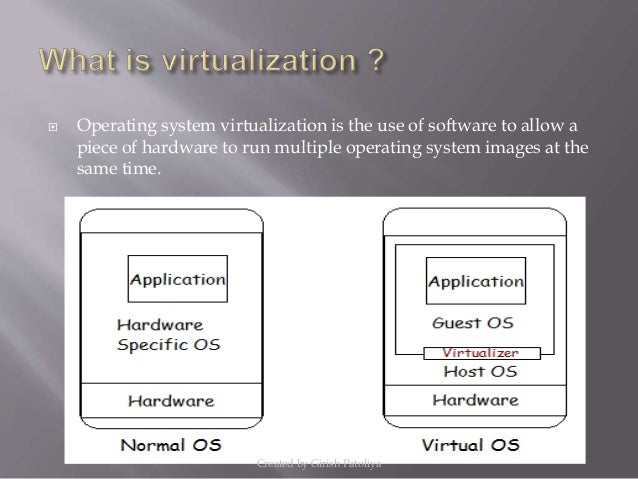
This can be easily tested with Buildroot qemu_x86_64_defconfig.Assuming the reader has little to no prior knowledge on the topic, this article will provide a step-by-step guide on how to create a Linux virtual machine (VM) using QEMU on a Windows system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
